Introduction of Research
Computational Science 4/4
|
<=PREV
| NEXT=> |
In the simulation of electrical and mechanical phenomena
of the heart, we eventually encounter problems with repeatedly solving large-scale
simultaneous equations with millions or tens of millions of dimensions.
The part of the simulation program which solves the simultaneous equations
is called Solver. Large-scale simultaneous equations are usually solved
using iterative methods, but because of the properties of the physical phenomenon
and the employed numerical method, the mathematical characteristics of the
coefficient matrix change significantly. A strategy to develop an optimal
solver is therefore important. As a single processor is no longer enough
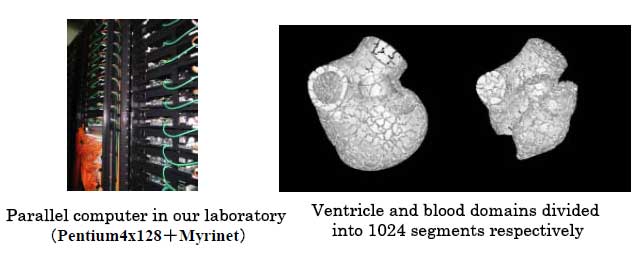
to deal with the whole heart, the domain is decomposed into many sections,
and parallel computations are performed with communication between neighboring
subdomains. This research is both mathematically interesting and of practical
importance. Eventually, collaboration will be required between computational
science and computer science. The figure on the right shows the decomposed
domains for massive parallel computations.
All Rights Reserved,
Copyright(C)2013, UT-Heart Laboratory
|

